Connected Factory and Smart Manufacturing Technologies
Click to zoom in
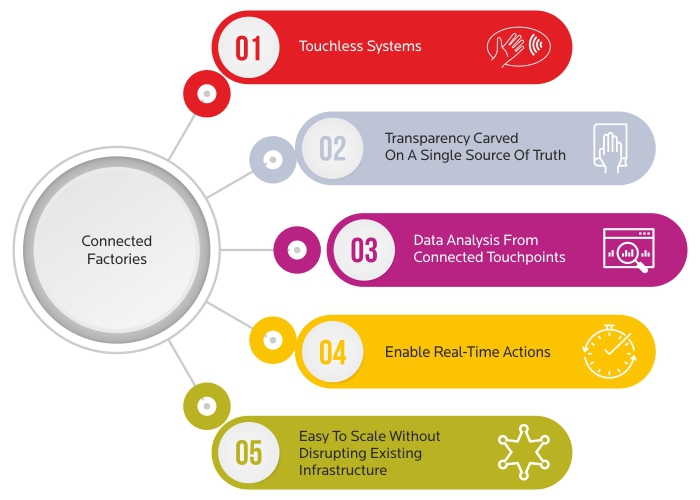
Top Benefits of Building Connected Factories
Powered by the next-gen technologies, '
Connected Factories' is the future that most businesses aim at, and some are already on their way to adoption. What are the benefits of having such a concept in place?
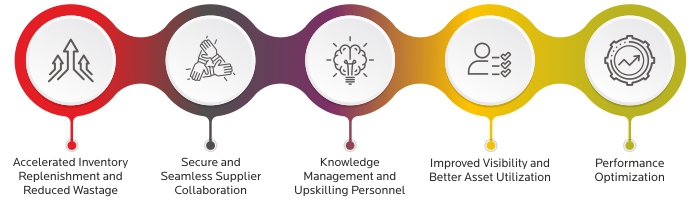
Accelerated Inventory Replenishment and Reduced Wastage
Companies can save up to 3% of the logistics cost, reducing event adversities by 18% through automated replenishment and accurate forecasting. Connected Factories does demand and supply planning well in advance instead of waiting for an order to come in and initiate the procurement cycle. This leads to warehouse space optimization and reduction of wastes.
Secure and Seamless Supplier Collaboration
Connected Factories opened gateways to B2B2C business model operations, where transactions happen through multiple suppliers' interactions. Blockchain-enabled smart contracts thus bind them together, securing every move and maintaining complete transparency with the stakeholders at play.
Knowledge Management and Upskilling Personnel
The wave of evolution must touch every shore, and in the case of "Connected Factories," every employee and stakeholder should be equipped to ride them smoothly. Using Augmented Reality, the workforce could be trained on the nitty-gritty of the operations, technological innovations, and their multifaceted role. Re-skilling, upskilling and safe monitoring of workforce to prepare them well through the journey.
Improved Visibility and Better Asset Utilization
One of the key benefits of having an IoT system is enabling real-time data transmission and views. Asset tracking, product design and development, quality checks, the evolved technologies display a clear and condensed dashboard for multiple touchpoints.
Performance Optimization
Increased real-time visibility and transparency enables system and operations performance optimization. Asset and system operating conditions are dynamically adapted to process disturbance and variability for optimal operational cost, process quality, output performance.
Benefits of Building Connected Factories
Click to zoom in
Challenges in Building Connected Factories
Though digital transformation in smart manufacturing is radical and the shift is happening rapidly, companies are slowly embracing it. They are, however, gearing up for the change. Following are the
major challenging areas that are acting as the speed breakers:
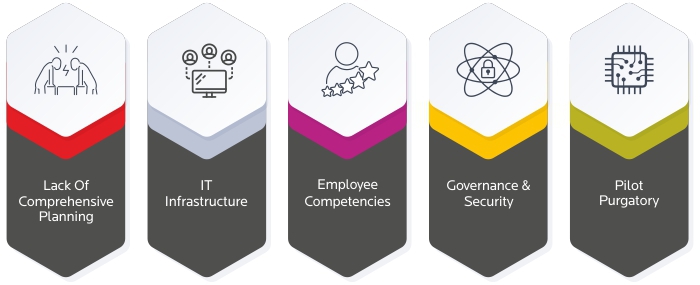
Lack Of Comprehensive Planning
Strategizing the transformation process is the step to start with. Establishing a clear vision and a phase-wise roadmap is essential to help manufacturing entities adopt technology faster. Too many companies are implementing too much technology without a plan that ultimately fails to create enough value in the long run. This is a massive waste of time, money, and resources. Instead, creating an ROI blueprint and demonstrating use cases priority-wise would add to organizational health, helping in holistic growth.
IT Infrastructure
Often even with a strategy in place, a company digress from the concern areas for the lack of technological backup and infrastructure. Right after setting clear goals and identifying the roadmap, the next thing to consider is the technology stack and ecosystem on which the organization is operating. Secure, comprehensive, scalable, and an analytics-based tech framework will be a booster for seamless adoption.
Employee Competencies
As much as manufacturers are enthusiastic about going for a technology overhaul, it is equally essential to prepare their workforce for the change. Not every employee will be tech-savvy and share the same level of understanding. Forming better partnerships, conducting training programs, continuous upskilling, and reskilling would help companies overcome this roadblock.
Governance & Security
Every technological move is based on a certain degree of compliance. Often there are strict guidelines that slow down the pace of implementation and integration. For instance, cloud-based technology must be GD/PR compliant and meet all the regulatory standards before integration.After all, confidential and vulnerable data sharing takes place at every level, and the matter of privacy in this regard is of prime importance.
Pilot Purgatory
All the above processes are time-consuming, and even everything is at its place, organizations conduct pilots before rolling out the innovations. Often things get stuck right after the pilots, and a movement from there on becomes a challenge.
Mobilizing the organization and following the top-down approach for driving transformation might be a practical move. Decentralized decision-making where decisions happen at every level might help to accelerate and turn your factory into the factory of the future.
Challenges in Building Connected Factories
Click to zoom in
Examples of Connected Factories
AI, robotics, and automation have been popular in industrial manufacturing for decades. However, there has been a significant technological disruption in the past year. A new wave of opportunities could be spotted, reducing the cost of technology integrations, growing functionalities, and expanding environments in which these new-age technologies could thrive effectively. Let's see how two major manufacturing industries are using technology to establish Connected Factories.
Automotive and Aerospace Manufacturing
Not just the top-notch IT houses, Boeing is also turning to digital manufacturing for better innovations, reduced shipping costs, and a quick go-to-market. A digital record system helps trace parts that are used on other planes, refurbished and put on another plane. Digital tools allow an effective field-force optimization scheduling and managing repair and maintenance of field personnel. Automated decision-making with advanced warehouse maintenance reduces costs and ups the inventory levels. Digital records are maintained to improve 'first-time performance.' The utilization of 3D printing for low-volume serial parts allows for last-minute deliveries and minimizes inventory. Manufacturers can predict ancillary failures, reducing maintenance and on-ground repair cost. Digital assets for maintenance like instructions, e-mails, and manuals are created for compliance purposes and easy reference guides. High-speed flight data transference enabling faster decisions and dispatch of schedules, list of components, repair histories, and tail numbers. Automation of receiving, storing, and deploying solutions improving productivity. Predictive supply chain enabling inventory replenishment, delivery time lags, and prepare accordingly.
Cement Manufacturing
Cement factories consist of aggressive activities and the movement of pieces. At the fundamental level,
predictive maintenance brings all together. Vibration analysis monitors assemblies in kiln drives, crushers, screens, conveyor belts, raw mills, separators, and blowers. Potential faults are predicted, and real-time anomaly detection helps in successfully diagnose the manufacturing systems. Many cement manufacturers over-deliver on their SLA quality due to the inability to track a batch's quality. Deploying neural network soft sensors and kiln activity monitoring accurately predicts a batch's quality mapping the best and worst-case scenarios as the cement industry goes through a paradigm shift and moves to a greener Cement 4.0 phase with the adaptation of condition monitoring sensors with real-time predictive analytics optimizing Yield, Energy and Throughput performance from Mines to Mills.
The Future of Connected Factories
This is the starting point of Industry 4.0 and the inception of the concept of Connected Factories. Succeeding in Industry 4.0 and digitalization is more than just about having the right IT tools. Strategizing this transformation is of utmost importance for better efficacy. To successfully run a Connected Factory, connectivity, intelligence, and flexible automation must be ensured across multiple verticals of manufacturing and supply chain distribution.
Connected Factories are the new future of the manufacturing industry. Not all can be integrated at once. However, deploying technology in a phased manner would help manufacturers to develop the factory of the future.