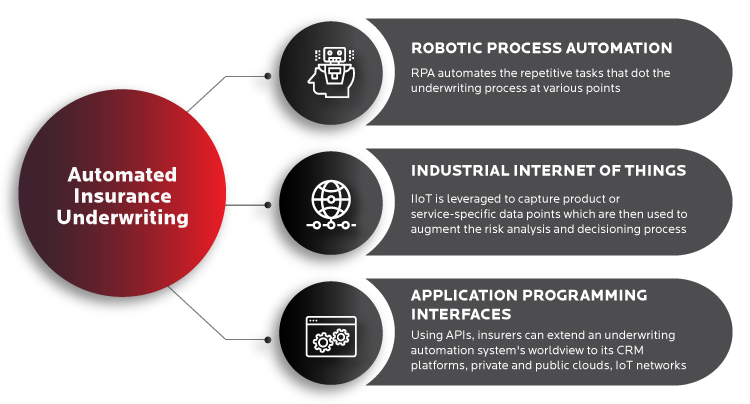
What is Automated Underwriting in Insurance?
Traditionally, insurance companies relied on underwriting experts and risk managers for risk assessment, premium pricing, and insurance application decisions. However, these processes were paper-based until the 2000s, after which insurers began adopting a variety of digital tools to support these processes through manual underwriting. However, manual underwriting models come to the company at major costs - the cost of underwriting can range as high as $50-130/hr, multiplying on a headcount basis in some lines of business, and the underwriting process can take anywhere from days to weeks. Moreover, scaling up with manual underwriting comes at high fixed costs in addition to increased operational overheads.
Automated insurance underwriting was designed to solve these problems. It relies on an integrated IT infrastructure, a comprehensive customer (and/or ecosystem) data footprint, and the company's underwriting rules to automate the underwriting process. In very simple terms, automated underwriting leverages artificial intelligence (AI), robotic process automation (RPA), natural language processing (NLP), optical character recognition (OCR), and accesses real-time data from 3rd parties using APIs - in order to map the risk profile associated with an asset or a scenario in the purview of your company's business rules. This results in instant decisioning on applications that earlier took days to assess - in addition, automated underwriting improves accuracy, eliminates bias, and significantly reduces costs associated with a traditionally cost-heavy process in this industry.
How Does Automated Underwriting in Insurance Work
To understand how automated underwriting works, imagine a black box, which takes in all the data associated with an application and outputs a premium price associated with the coverage of a certain risk. So what is happening inside the black box? First, an automated insurance system must be supplied with the business rules that align with an insurer's risk management strategy and the overall business strategy. While some automated insurance systems allow insurers to implement their underwriting process by tweaking the settings in an on-prem or cloud-based application, new age systems rely on the insurer's past data and learn sophisticated rules and knowledge used by their underwriters.
Automated underwriting relies on a baseline degree of IT maturity in order to make it profitable and extract maximal value for the insurer's bottom-line. As more and more insurers are going digital and taking up an ecosystem view in their IT strategy, automated underwriting systems can be implemented faster by making use of API-based design to pipeline the application data and environment variables surrounding a risk. Underwriting rules learned from the insurer's past records are then applied to this data to output a decision on the application, the associated degree of risk, amount of coverage, and the cost of premium based on the risk profile that an application represents.
How Do Automated Underwriting Systems in Insurance Work
At the heart of automated underwriting systems is AI, which mimics the most mathematically sophisticated and experienced underwriters' capabilities in an insurance ecosystem. To make this possible, various automated systems make use of different architectures - while some rely on separate intelligent modules to measure the risk of an application and predict the output variables, others make use of integrated intelligence logic to do the same. However, risk analysis and determination of underwriting terms are usually present as separate problems inside an insurance underwriting system - specifically because of the benefits that a separate risk analysis module brings for applications on which your underwriting system is inconclusive.
The design and nature of intelligence within an automated underwriting system depends on the line of business that it aims to serve. For instance, while evolutionary algorithms and fuzzy logic rule engines demonstrate better health insurance underwriting performance, markovian models make more sense in the auto insurance line. Moreover, some product lines also rely on language inference systems to infer quantitative parameters from qualitative parameters.
How To Measure The Success Of Underwriting Automation in Insurance
According to Mckinsey, the best-automated underwriting systems combine the best of analytics and human judgment to maximize the value for an insurer. As a result, assessing a system based on the degree of intervention it requires in underwriting alone is not the right approach to assessing such a system's effectiveness. Instead, automated underwriting must be measured along with these three parameters:
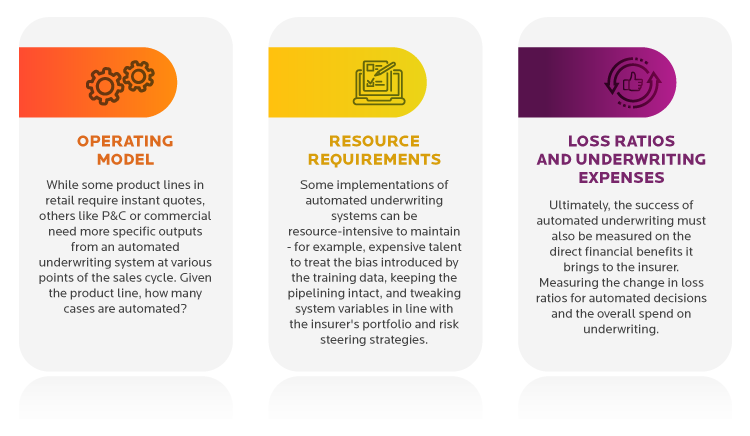
- How it augments the operating model: While some product lines in retail require instant quotes, others like P&C or commercial need more specific outputs from an automated underwriting system at various points of the sales cycle. Given the product line, how many cases are automated?
- Maintenance resource requirements: Some implementations of automated underwriting systems can be resource-intensive to maintain - for example, expensive talent to treat the bias introduced by the training data, keeping the pipelining intact, and tweaking system variables in line with the insurer's portfolio and risk steering strategies.
- Change in loss ratios and underwriting expenses: Ultimately, the success of automated underwriting must also be measured on the direct financial benefits it brings to the insurer. Measuring the change in loss ratios for automated decisions and the overall spend on underwriting.
Measuring Underwriting Automation Effectiness in Insurance
Generally, automated underwriting systems bring millions of dollars in cost benefits, reduce turnaround time by over 95%, and can infer thousands of unique rules when implemented in large-scale contexts.
How Accurate Is Automated Underwriting in Insurance
When implementing automated underwriting systems, insurers usually take a staggered approach to increasing the fraction of cases that can be automated. Most implementations bring near-complete accuracy (up to 100%) to the automated applications - the cases on which the system remains indecisive are rerouted to expert underwriters. However, the best implementations aim to bring complete accuracy to the automated applications while minimizing the fraction of cases that require human intervention.
However, there is another aspect to accuracy when it comes to underwriting. Mckinsey found that in the P&C line, a small business owner could get coverages that varied by 233% - against premiums that varied by only 24% across five providers. In automated systems, optimal performance can be achieved by improving the input parameters and fine-tuning the risk analysis model to account for these parameters. For example, if a driver clocks thousands of miles on a personal vehicle without a history of accidents or claims, then such a customer could be offered reduced premiums based on this data. Therefore, optimized premium and coverage amounts are a crucial aspect of a high-accuracy underwriting process - and ultimately depends on how accurately the model assesses the risk associated with an asset/scenario in reality.
Why Use Automated Underwriting System in Insurance
Automated underwriting brings several benefits to insurers that currently rely on manual underwriting. While reduced underwriting expenses are a direct incentive for insurers to leverage automated underwriting, here are a few more benefits:
- Utilize resources in an optimal manner: While the complexity of applications may vary over the course of your operations, your underwriters are ultimately trained to handle the most complex of them. By automating underwriting for low-complexity cases, your underwriters tend to focus on the most difficult problems while the system takes care of the business-as-usual.
- Bring cutting-edge CX to your offerings: Speed of response is one of the first things that customers want from their businesses today. Automated underwriting helps you render decisions on applications within seconds - with the added scope of personalizing premiums and coverage by the customer's preferences while building profitability for the business in a sustainable fashion.
- Additional benefits: Automated underwriting also brings uniformity to the business rules that drive day-to-day operations and reduces manual errors involved in the process. Moreover, it also brings real-time visibility to your risk exposure, augments top-level decisions with live KPIs and manual processes with signals that can reduce efforts associated with quantitative analysis in complex application scenarios.
Insurance Underwriting Automation Examples in Insurance
Here are some of the most innovative underwriting automation examples from the industry:
- One of the first underwriting automation efforts were made in the 1990s -where a fuzzy logic rules engine (FLRE) was designed to infer rules from a health insurer's past underwriting records, and an evolutionary algorithm was used to optimize the model's performance. Post-implementation, 19% of applications were handled by the system with a zero-touch process.
- In a recent underwriting automation implementation, a term insurance provider relied on complex machine learning models to automate underwriting for most applications. However, it also leveraged a risk assessment mortality model to infer whether an application is eligible for the automated processing track or not - thereby delivering on their CX promises in a more honest fashion.
- A leading global reinsurance leader recently rolled out an insurance underwriting automation capability targeted at insurance providers operating in the African markets - where the features leveraged by underwriting automation stand largely missing/irrelevant/unrecorded. To make automated underwriting possible, the company deployed complex extrapolation models that are fine-tuned to output underwriting decisions based on limited features and as little as 15,000-20,000 data points.