Cloud has touched upon almost all the business nuances adding a significant thrill to data and analytics. Capabilities, tools, and support offered by modern databases on current cloud technology are much ahead of times than the on-premise technology. On this note, let’s dive deeper to understand what Cloud Data Management is.
Cloud Data Management is how data is managed across cloud-based platforms, with or without on-premise storage in place. Cloud is a valuable data storage medium for long-term archiving, backup, and disaster recovery. Compared to traditional data management methods, data stored in the cloud has its own set of rules for data integrity and security.
With cloud-based data management, resources can be purchased as and when needed. Data can be easily shared across private, public, and in between on-premise storage. While some platforms can manage and use data across cloud and on-premise environments, cloud data management ensures that the respective data are subject to entirely different practices. A Cloud Data Management model enables enterprises with convenient data access under built-in security. There’s a more substantial need to modernize traditional data management into a self-service data management model. Hence, the need for a robust and reliable Cloud Data Management Strategy.
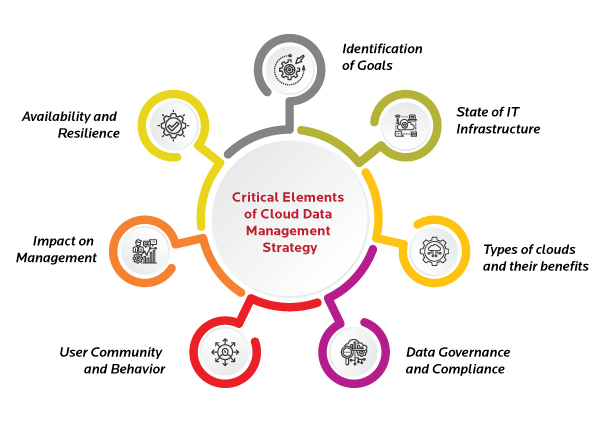
Critical Elements of Cloud Data Management Strategy
When it comes to data, it is best to have a strategy instead of ad hoc plans. Data Management covers all the proactive processes for data collection, organization, protection, sharing, and storing data. Businesses and enterprises that understand the importance of data-centric decision-making realize the need to have a strategy in place. So, what are the key elements of putting together a comprehensive data management strategy?
Identification of Goals
Your organization is operational on billions of data points every day. Thus, aligning your business goals and objectives is a must to avoid waste of resources and time. Your business goals form the core of your strategy. To keep things streamlined, it is advisable to focus on three to four company use cases that demand close attention for the quarter and start building a strategy from there.
State of IT Infrastructure
Once the quarterly goals are in place, businesses need to identify the tools and technology for process enhancement. Weaving the two can create the necessary framework. This is where you could identify what you already have and what you need to adopt a sturdy cloud data management system.
Types of Clouds and their benefits
No two clouds are the same! It is even better if businesses are aware of the different clouds and their utilization. There are public, private, community, and hybrid solutions available as per requirements. Let’s say the primary need of business is now scalability at lightning speed. Though a private cloud is agile enough and can go up and down with the changing requirements, a business needs to spend its entire CAPEX budget to purchase. A massive scale-out at a budget would require a public cloud. Cloud bursting could be a safer option to explore as you can switch between public and private clouds in times of intensive testing and development.
Data Governance and Compliance
HIPAA, FINRA, GLBA, PCI-DSS, SOX, and more such data governance and compliance frameworks come with their own set of challenges. Thus, businesses need to consider how cloud adoption can be smoother while following the necessary compliance guidelines. Security is a prime concern during cloud migration. The infrastructure layer mainly concerns with access and secured services through layering. Hence, understanding the cloud architecture that a business is being migrated to and what security policies it supports within the infrastructure are essential.
Critical Elements of Cloud Data Strategy
User Community and Behavior
Resources in production environments need a comprehensive overview of the management tools, security, resiliency, compliance, and availability. Focusing on these parameters is essential to keep the entire team engaged in the migration process.
Impact on Management
Adoption of any cloud technology means an overall disruptive change within the organization. The inclusion of vendors and external sites impacts workflow, control, monitoring, and other operational factors. Carefully considering how the businesses are going to react to the transforming framework is also a necessity.
Availability and Resilience
During recovery, availability and resilience are essential aspects to look at as cloud is needed for backup, data vaulting, and replication during a breakdown.